Hepatitis B is a severe liver infection caused by the Hepatitis B virus (HBV). It affects millions of people worldwide and poses a significant public health challenge, especially in countries like Bangladesh, where the infection rate remains considerable. At Pledge to Protect, we are committed to safeguarding lives through timely vaccination and raising awareness about preventable diseases like HBV.
What is Hepatitis B?
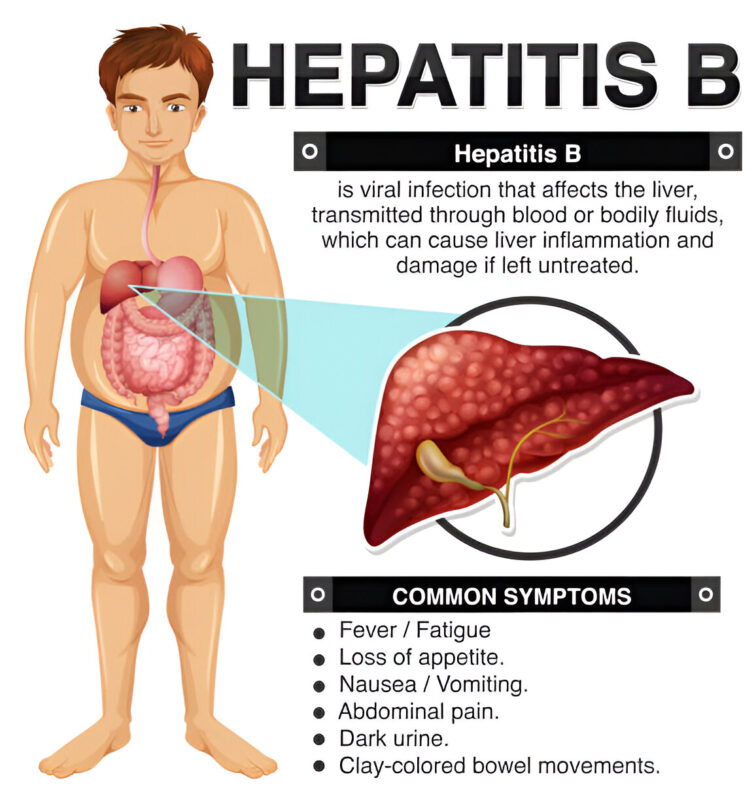
Hepatitis B is a contagious viral infection that attacks the liver, potentially causing acute (short-term) and chronic (long-term) illnesses. While some people recover completely without complications, others develop chronic HBV, which can lead to severe liver damage, cirrhosis, liver failure, or even liver cancer.
The virus spreads through contact with infected blood, bodily fluids (such as semen or vaginal secretions), or from mother to child during childbirth. Standard modes of transmission include:
- Unprotected sexual contact
- Sharing needles or syringes
- Unsafe medical procedures and blood transfusions
- From an infected mother to her newborn during delivery
Because many infected individuals show no symptoms, Hepatitis B can silently spread within communities, emphasizing the importance of vaccination and testing.
Symptoms to Watch For
Many people with HBV do not show symptoms initially, sometimes for decades, especially children. When symptoms do appear, they may include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain, particularly near the liver
- Dark urine and pale stools
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
If you experience these symptoms or suspect you have been exposed to HBV, seeking prompt medical advice is crucial.
The Role of Vaccination in Prevention
Prevention is the most effective way to combat HBV. The Hepatitis B vaccine is a safe, highly effective vaccine that stimulates the body’s immune system to fight the virus. When administered according to the recommended schedule—usually three doses—it provides long-lasting protection, often lifelong in healthy individuals.
Who Should Get Vaccinated?
- All newborns and infants (vaccination within 24 hours of birth is crucial)
- Children and adults who were not vaccinated as infants
- Healthcare workers and laboratory staff exposed to blood or body fluids
- People with multiple sexual partners or sexually transmitted infections
- People who inject drugs or share needles
- Family members or close contacts of HBV-infected persons
- Individuals with chronic liver disease or HIV
Vaccination not only protects the individual but also reduces the spread of HBV in the community.
Pledge to Protect: Making Vaccines Accessible
At Pledge to Protect, we specialize in supplying and distributing critical vaccines, including the Hepatitis B vaccine, ensuring they are available to healthcare providers and communities across Bangladesh. In partnership with Health Care Pharmaceutical, we are proud to deliver trusted vaccines that help prevent life-threatening diseases.
Our mission goes beyond simply supplying vaccines—we strive to educate communities about the importance of vaccination and encourage everyone to participate actively in disease prevention.
How You Can Help
- Get vaccinated if your child hasn’t yet received the HBV vaccine.
- Encourage family and friends to get vaccinated and tested.
- Practice safe behaviors such as using barrier protection during sex and avoiding needle sharing.
- Support public health initiatives aimed at increasing vaccination coverage and awareness.
- Get tested if you believe you might have been exposed so that you can get timely care.
Treatment and Living with Hepatitis B
Currently, there is no cure for chronic HBV, but antiviral medications can help manage the infection, reduce liver damage, and lower the risk of complications. Early diagnosis and regular monitoring are essential for people with Hepatitis B to maintain their health.
FAQs about Hepatitis B
Q: How is HBV transmitted?
Mainly through contact with infected blood, body fluids, unprotected sex, needle sharing, or from mother to child during birth.
Q: Can HBV be cured?
Acute HBV often resolves independently; chronic HBV can be managed but not cured.
Q: Is the HBV vaccine safe?
The vaccine is safe, effective, and recommended worldwide for all age groups.
Q: How many doses of the HBV vaccine do I need?
Typically, three doses are given over six months for complete protection.
Q: Can adults get vaccinated?
Vaccination is recommended for adults who missed the vaccine as children or are at higher risk.
Q: Is Hepatitis B standard in Bangladesh?
Yes, HBV is relatively common, making vaccination and awareness critical.
Q: Where can I get the Hepatitis B vaccine in Bangladesh?
Vaccines are available through government health programs, private clinics, and authorized suppliers like Pledge to Protect.
Final Thoughts
Hepatitis B remains a global health challenge, but with increased awareness, effective vaccination, and proactive prevention, it is a disease we can control and eventually eliminate. Taking the first step by getting vaccinated and spreading knowledge is key to a healthier future. Join Pledge to Protect in our mission to make vaccines accessible and save lives today for a healthier tomorrow.


One thought on “Hepatitis B | Symptoms and Causes 2025”